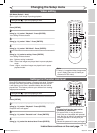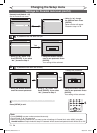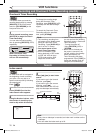
xxxx
Others
Glossary
Analog audio
An electrical signal that directly repre-
sents sound. In contrast, digital audio
which can be an electrical signal, but
is an indirect representation of sound.
See also Digital audio.
Aspect ratio
The width of a TV screen relative to its
height. Conventional TVs are 4:3 (in other
words, the screen is almost square);
widescreen models are 16:9 (the screen
is almost twice as wide as it is high).
Chapter
Just as a book is split up into several
chapters, a title on a DVD disc is usually
divided into chapters. See also Title.
Component video output
This is a video signal format that con-
veys each of three principal colors of
light (red, blue and green) through
different signal lines. This allows the
viewers to experience picture colors
as original as it is. There are several
signal formats, including Y/PB/PR and
Y/CB/CR.
CPRM (Content Protection for
Recordable Media)
This is a format used to record copy-
once programs. By recording coded data
on the area of DVD discs that ordinary
writing software cannot write on, it pre-
vents copy-once programs from being
recorded repeatedly on different media.
Digital audio
An indirect representation of sound by
numbers. During recording, the sound
is measured at discrete intervals (44,
100 times a second for CD audio) by
an analog-to-digital converter, generat-
ing a stream of numbers. On playback,
a digital-to-analog converter generates
an analog signal based on these num-
bers. See also Sampling frequency and
Analog audio.
Dolby Digital
The system developed by Dolby
Laboratories to compress digital sound.
It offers you sound of stereo(2ch) or
multi-channel audio (up to 5.1ch).
Finalize
To make recorded contents on DVD
discs possible to be played back on
DVD players. With this unit, it is pos-
sible to finalize DVD-RW/DVD-R discs.
MP3 (MPEG Audio Layer 3)
MP3 is a method of compressing files.
You can copy MP3 files on CD-RW/R
discs from the computer and play back
the files on this unit.
PCM (Pulse Code Modulation)
PCM is a format that converts audio
into digital data. It is mainly used for
Audio CDs and DAT. This unit can play
back sounds as realistic as possible
by converting even compressed Dolby
Digital and MPEG audio to PCM.
Playlist
From this list you can play back con-
tents of a disc in your desired order or
sequence. Also it allows to search a
specific scene directly.
Progressive Scan (525p/480p)
A type of display that does not split
each frame into fields, and instead
scans directly through all the scanlines
of each frame in order. Progressive
Scan provides less flickering and
higher image resolution than tradi-
tional (525i/480i) TV signals. Refer to
page 15 for instructions on selective
Progressive Scan mode.
Regions code
Regions associate discs and players
with particular areas of the world. This
unit will only play back discs that have
compatible region codes. You can find
the region code of your unit by looking
at the rear panel. Some discs are com-
patible with more than one region (or
all regions).
Sampling frequency
The rate which sound is measured by
a specified interval to turn it into digital
audio data. The numbers of sampling
in one second defines as sampling fre-
quency. The higher the rate, the better
the sound quality is.
SAP (Secondary Audio Program)
Sub audio channel which is delivered
separately from main-audio channel.
This audio channel is used as an alter-
nate in bilingual broadcasting.
S-Video output
It delivers independently each signal
of color(C) and luminance(Y) to TV as
video signals, so that higher-quality
picture will be materialized.
Title (DVD only)
A collection of chapters on DVD disc.
See also chapter.
Track
Audio CDs use tracks to divide the
content of a disc. The DVD equivalent
is called a chapter. See also Chapter.
Language code
Language Code
Abkhazian 4748
Afar 4747
Afrikaans 4752
Albanian 6563
Amharic 4759
Arabic 4764
Armenian 5471
Assamese 4765
Aymara 4771
Azerbaijani 4772
Bashkir 4847
Basque 5167
Bengali;Bangla 4860
Bhutani 5072
Bihari 4854
Bislama 4855
Breton 4864
Bulgarian 4853
Burmese 5971
Byelorussian 4851
Cambodian 5759
Catalan 4947
Chinese 7254
Corsican 4961
Croatian 5464
Czech 4965
Danish 5047
Dutch 6058
English 5160
Esperanto 5161
Estonian 5166
Faroese 5261
Fiji 5256
Finnish 5255
Language Code
French 5264
Frisian 5271
Galician 5358
Georgian 5747
German 5051
Greek 5158
Greenlandic 5758
Guarani 5360
Gujarati 5367
Hausa 5447
Hebrew 5569
Hindi 5455
Hungarian 5467
Icelandic 5565
Indonesian 5560
Interlingua 5547
Interlingue 5551
Inupiak 5557
Irish 5347
Italian 5566
Japanese 5647
Javanese 5669
Kannada 5760
Kashmiri 5765
Kazakh 5757
Kinyarwanda 6469
Kirghiz 5771
Kirundi 6460
Korean 5761
Kurdish 5767
Laothian 5861
Latin 5847
Latvian; Lettish 5868
Lingala 5860
Language Code
Lithuanian 5866
Macedonian 5957
Malagasy 5953
Malay 5965
Malayalam 5958
Maltese 5966
Maori 5955
Marathi 5964
Moldavian 5961
Mongolian 5960
Nauru 6047
Nepali 6051
Norwegian 6061
Occitan 6149
Oriya 6164
Oromo (Afan) 6159
Panjabi 6247
Pashto; Pushto 6265
Persian 5247
Polish 6258
Portuguese 6266
Quechua 6367
Rhaeto-Romance 6459
Romanian 6461
Russian 6467
Samoan 6559
Sangho 6553
Sanskrit 6547
Scots Gaelic 5350
Serbian 6564
Serbo-Croatian 6554
Sesotho 6566
Setswana 6660
Shona 6560
Language Code
Sindhi 6550
Singhalese 6555
Siswat 6565
Slovak 6557
Slovenian 6558
Somali 6561
Spanish 5165
Sundanese 6567
Swahili 6569
Swedish 6568
Tagalog 6658
Tajik 6653
Tamil 6647
Tatar 6666
Telugu 6651
Thai 6654
Tibetan 4861
Tigrinya 6655
Tonga 6661
Tsonga 6665
Turkish 6664
Turkmen 6657
Twi 6669
Ukrainian 6757
Urdu 6764
Uzbek 6772
Vietnamese 6855
Volapuk 6861
Welsh 4971
Wolof 6961
Xhosa 7054
Yiddish 5655
Yoruba 7161
Zulu 7267
E9A10UD_DVR90VG.indd 82 2005/12/26 18:56:21